
We investigated the overlooked attribute confusion problem in T2I evaluation.

We investigated the overlooked attribute confusion problem in T2I evaluation.

We introduced a new human evaluation protocol to capture fine-grained localization.

We proposed L-VQAScore, that effectively mitigates attribute confusion in T2I evaluation.
Attribute confusion occurs when a visuo-textual model misassigns attributes to irrelevant regions within an image, resulting in semantically inaccurate results. While the attribute confusion problem impacts T2I generative models, its automated evaluation requires metrics effectively recognizing correct entity-attribute associations - this is underexplored.
We examined how state-of-the-art T2I evaluation metrics handle attribute confusion in the paper. As revealed in recent work, VLMs exhibit behaviors akin to bag-of-words models in cross-modal understanding. Thus, they are limited in evaluating compositional semantics with complex entity-attribute bindings, which can be very critical for T2I in domains like fashion. Recent VQA-based metrics have enhanced the evaluation of entity-attribute binding by checking whether each attribute is correctly reflected on its corresponding entity. However, as highlighted by our preliminary evaluation, existing T2I metrics struggle to recognize attribute confusion cases, in other words, when the attributes are reflected on the wrong entities.
In this paper, we propose an improved human evaluation protocol and an automatic T2I evaluation method in assessing complex prompts with fine-grained semantics. Particularly, we focus on measuring attribute confusion: when a model generates correct entities/attributes, but they are associated incorrectly.
To measure the alignment between the conditioning prompt and the generated image, we represent the conditioning text into structured entity-attribute pairs. L-VQAScore localizes regions of interest leveraging entity categories via a semantic segmentation module. Then reflection and leakage questions are composed to evaluate the presence of desired and leaked attributes in the localized regions, accounting for both attribute depiction and localization.
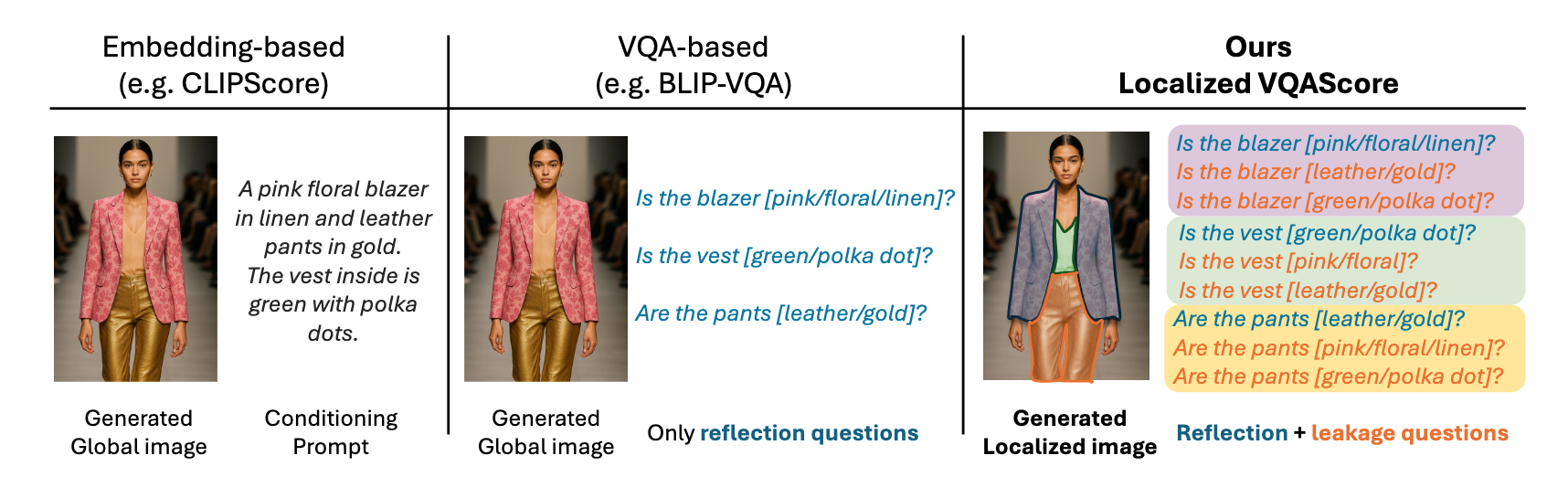
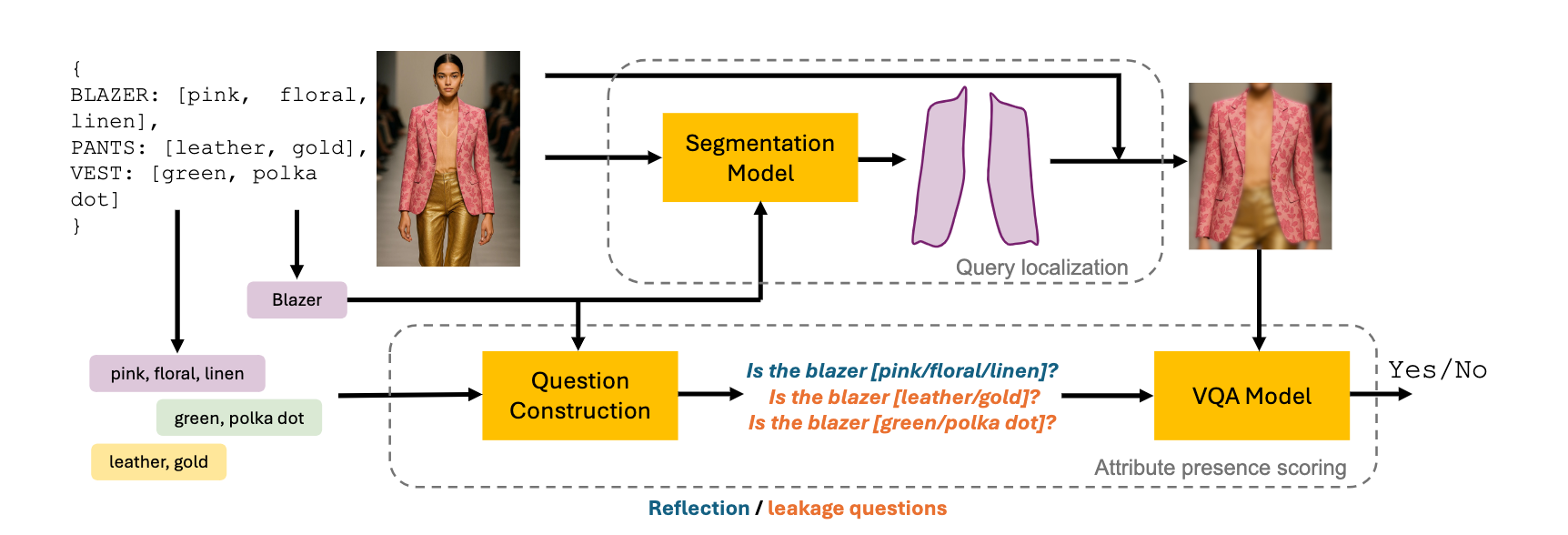
Figure 1: L-VQAScore approach.
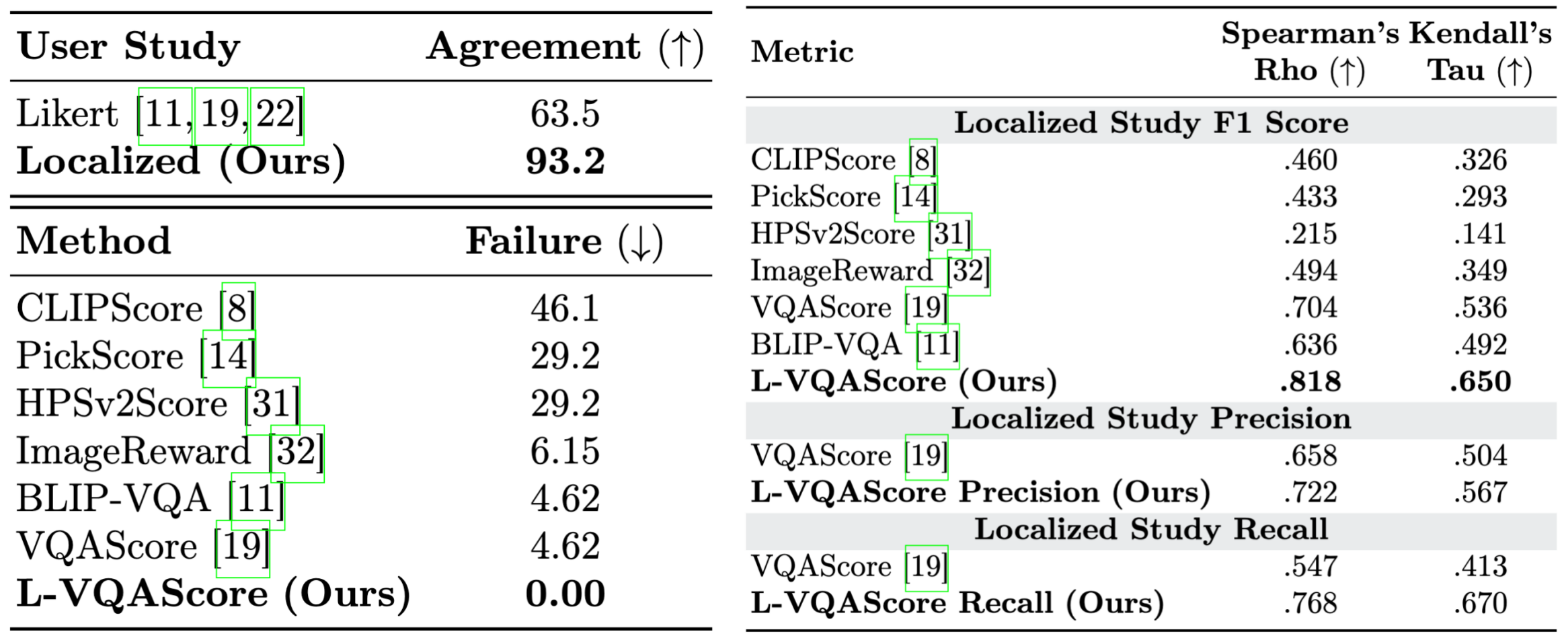
Figure 2: Left Top: Agreement rates for user human evaluation studies. Left Bottom: Failure rate of current T2I evaluation metrics, measured as the percentage of test cases where attribute-swapped pairs receive higher scores. Right: Performance in T2I alignment regarding the localized study F1 Score, Precision and Recall. L-VQAScore consistently surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods.
We direct interested readers to our recent research for investigation into text-to-image generation with enhanced localization and controllability: LOTS of Fashion! Multi-Conditioning for Image Generation via Sketch-Text Pairing (ICCV25)
@inproceedings{liu2025evaluating,
title={Evaluating Attribute Confusion in Fashion Text-to-Image Generation},
author={Liu, Ziyue and Federico, Girella and Yiming, Wang and Davide, Talon},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing},
year={2025},
}